Reducing Environmental and Occupational Cancer Risks Toolkit
Module 5: Advancing Health Equity with Environmental Justice
3. TOOLS FOR TAKING ACTION
State cancer programs routinely examine disparities in cancer incidence rates to help target intervention strategies. Examining disparities related to exposures is another method to identify priorities for cancer risk reduction strategies.
There are online tools available to identify places where environmental exposures disproportionately burden communities to support cancer risk reduction actions. These environmental justice tools can assist efforts described in Module 2 to identify problematic cancer risks confronting non-white, low income, refugee and indigenous communities.

CDC’s Environmental Justice Dashboard is used to explore data on environmental exposures, community characteristics, and health burden — factors important to understanding and addressing environmental justice issues. Users of this tool type their zip code into the search bar, then are provided with information related to their community characteristics, environmental exposures, and environmental justice indices. Although health burdens are addressed in this tool, cancer is not an outcome addressed, but the tool can still be utilized to understand environmental exposures of interest and concern.
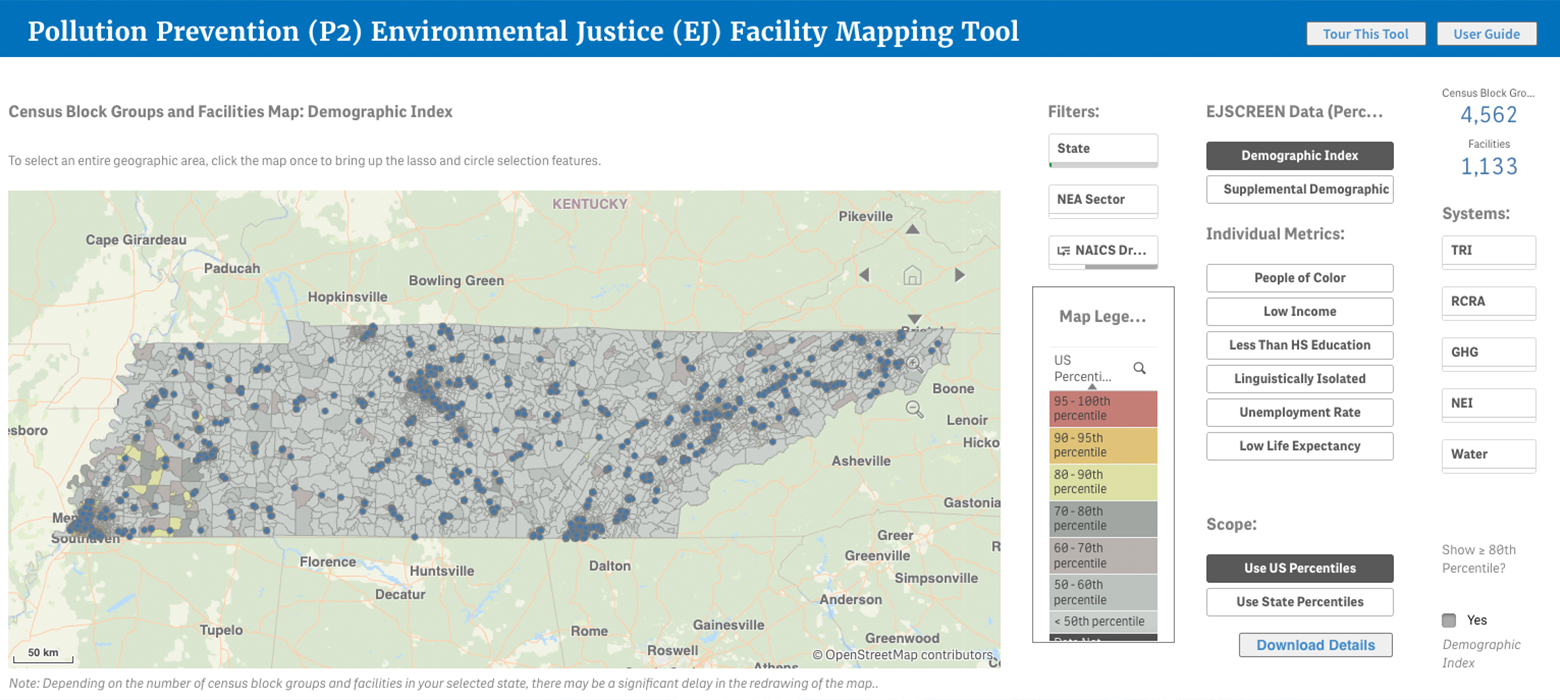
As discussed in Module 2, to support a reduction in health, social and ecological inequalities, the U.S. EPA developed the EJScreen, a mapping and screening tool that reveals patterns in environmental inequalities related to where people of color and/or low-income populations reside. EJScreen users select a geographic area; the tool then provides socioeconomic, demographic, and environmental quality indicators for that area.
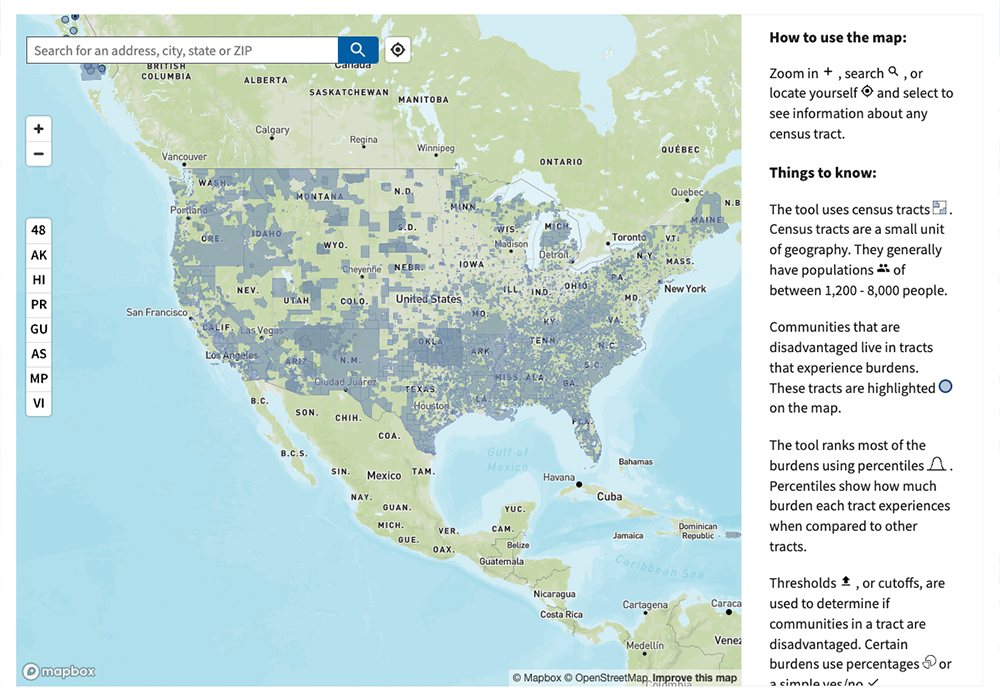
The CEJST is a geospatial mapping tool that identifies areas across the nation where communities are faced with significant and disproportionate environmental burdens. These burdens are organized into eight categories: climate change, energy, health, housing, legacy pollution, transportation, water and wastewater, and workforce development.
Click here to watch a 9 minute tutorial on how to use CEJST.
The tool highlights disadvantaged census tracts across all 50 states, the District of Columbia, and the U.S. territories. Communities are considered disadvantaged if they are:
The methodology and detailed categories of burden can be found here.

[Click here to watch a 6 minute tutorial on how to use the P2 EJ Facility Mapping Tool.]
The P2 EJ Facility Mapping Tool helps to geographically target facilities in or adjacent to underserved communities within U.S. EPA’s pollution prevention program’s five industrial sector-based National Emphasis Areas (NEAs), which include:
