Getting Started with the Whole School, Whole Community, Whole Child (WSCC) Model
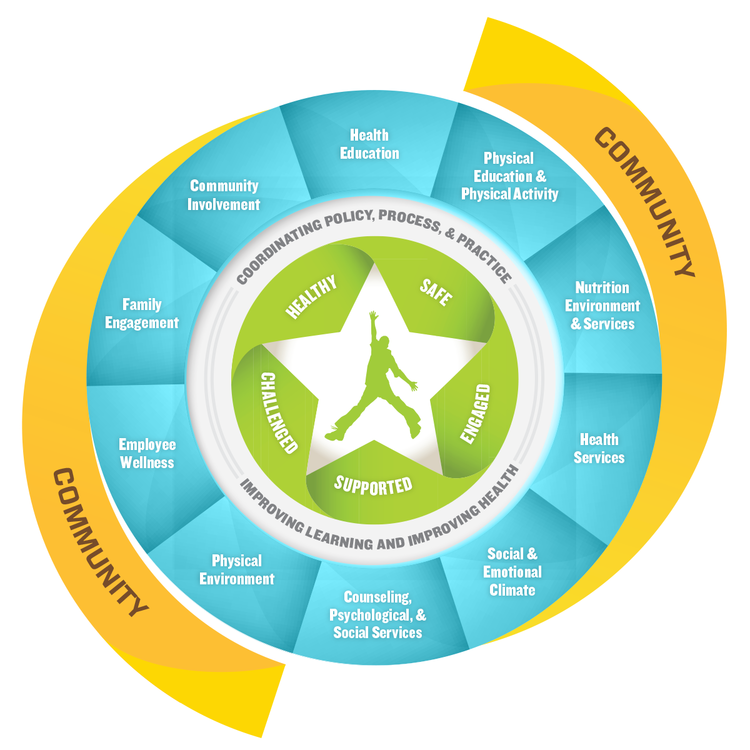
The Whole School, Whole Community, Whole Child (WSCC) model, developed by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development (ASCD), is an expansion of the earlier Coordinated School Health approach. It emphasizes the need for collaboration between education and health sectors to ensure each child is healthy, safe, engaged, supported, and challenged. It is foundational to effective, comprehensive school-based mental health solutions.
Why?
- Integrated Focus: It recognizes the interconnectedness of physical, emotional, and mental health in students’ development and academic success.
- Collaborative: It encourages collaboration among school and district staff, families and caregivers, students, and community partners.
- Preventative and Responsive: It focuses on using evidence-based interventions while also emphasizing preventative measures through safe and supportive learning environments, nurturing adult relationships, and promoting health behaviors.
- Inclusive and Equity-Driven: It promotes inclusivity and equity, ensuring mental health services and support are accessible to all students, regardless of their background or circumstances.
- Sustainable: It embeds mental health within the broader context of school health, creating a more sustainable approach to student well-being.
Developed by Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
https://www.cdc.gov/healthyyouth/wscc/model.htm
This page includes an overview of the WSCC model, a breakdown of each of the model’s core components, and tools for getting started.
Developed by the National Association of Chronic Disease Directors (NACDD)
https://chronicdisease.org/resource/resmgr/school_health/wscc_ppt_and_speaking_point.pptx
This ready-to-use PowerPoint presentation provides an overview of the WSCC model and can be modified to meet the individual needs of your school or district.
Developed by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
https://www.cdc.gov/healthyschools/vhs/index.html
This tool demonstrates how the Whole School, Whole Community, Whole Child (WSCC) model shows up in every area of the school building, from the classroom to the playground to the staff lounge and more. It also provides a comprehensive list of resources for each area of the WSCC model.
Healthy Schools Roadmap (developed by the National Healthy Schools Collaborative)
https://www.healthyschoolsroadmap.org/
- This Roadmap outlines priorities, opportunities, and case studies to support healthy schools from a federal, state, and local perspective (district/school).
WSCC Practice Blueprint (developed by the UCONN Collaborative on School and Child Health)
https://csch.uconn.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/2206/2022/08/CSCH-WSCC-Practice-Blueprint.pdf
- This Blueprint takes school health teams through a ten-step process to improve their practice alignment with the WSCC model. It includes resources related to teams, resource mapping, assessment, advocacy, and more.
WSCC Practice Briefs (developed by the UCONN Collaborative on School and Child Health)
https://csch.uconn.edu/wscc-practice-briefs/
- These briefs provide an overview of the evidence supporting each component of the WSCC model and concrete strategies (broken down by the level of effort needed) to strengthen that model component.
WSCC Team Training Modules (developed by the Society of Public Health Education)
- The WSCC Team Training Modules are ready-made professional development resources for states, districts, or local schools to build, strengthen, and sustain school teams implementing the WSCC model.

No matter the framework used in your school community, aligning the WSCC model as a foundation ensures a holistic approach that addresses all aspects of student well-being and promotes a unified and comprehensive strategy for mental health support in schools.
Explore how to align the WSCC model with comprehensive school-based mental health and other commonly used frameworks below. Continue reading to discover a breakdown of these frameworks and resources for effective implementation.
WSCC & Mental Health Strategy Guide & Reflection Tool
Developed by the National Association of Chronic Disease Directors (NACDD)
This tool identifies the connection between mental health and each component of the WSCC model and provides concrete strategies for how mental health supports each area of WSCC. Teams in schools can use the template worksheets at the end of the resource to outline how they can integrate mental health into the WSCC model, considering their unique programs, practices, and community needs.
Using the WSCC Model to Support Mental Health in Schools
Developed by the National Center for School Mental Health (NCSMH)
This one-page document outlines how your district can align school mental health efforts within the context of the WSCC model.
Using the WSCC Model to Integrate Social and Emotional Learning in Schools
Developed by RMC Health and the Colorado Department of Education Wellness Unit
This guide provides an overview of opportunities to integrate social-emotional learning into all components of the WSCC model to ensure as systemic approach.
Addressing SEL through the WSCC Model
Developed by the Society of Public Health Education (SOPHE)
This guide provides school health staff and school health teams with beginning support for integrating SEL competencies into the WSCC model through a series of simple handouts and suggested tools.
Connecting SEL with Other School-Based Frameworks
Developed by the Collaborative for Academic, Social, and Emotional Learning (CASEL)
This brief resource guide looks at SEL within the context of two commonly used school-based frameworks – MTSS and PBIS
Integrating SEL Within MTSS To Advance Equity
Developed by the Center on Multi-Tiered Systems of Support
This toolkit supports state and district leaders in integrating equity-focused SEL into a multi-tiered system of supports (MTSS).
Working Together: SEL and Multi-Tiered System of Supports
Developed by the Council of Chief State School Officers
Webisode series, “Effective Multi-Tiered System of Supports for Whole Child Development” to support states in the process of integrating SEL and whole child development more fully into their multi-tiered system of supports frameworks.
Integrating SEL into your School-Wide PBIS Framework
Developed by the Center on Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports
A quick guide that explores strategies and best practices for integrating SEL into school-wide PBIS.
Teaching Social-Emotional Competencies within a PBIS Framework
Developed by the Center on Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports
This overview document combines current research with strategies and best practices for teaching social-emotional competencies within a PBIS framework with recommendations for district and school staff.
Multi-Tiered System of Supports (MTSS) in the Classroom
Developed by the Center on Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports
This practice guide explores the implementation of PBIS across multi-tiered systems of support.
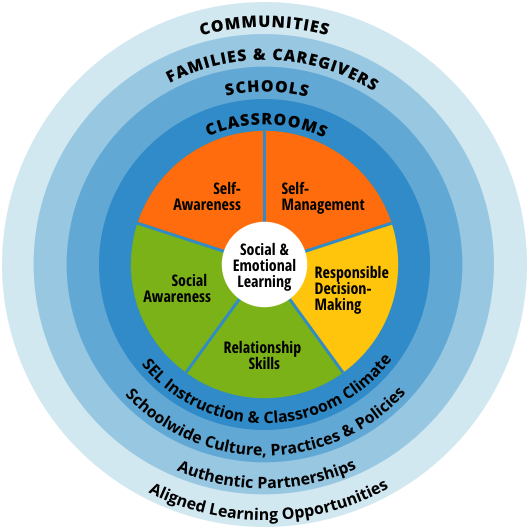
Social-Emotional Learning
The Collaborative for Academic, Social, and Emotional Learning (CASEL) framework, which centers around five core competencies, is a widely recognized approach for promoting social and emotional learning (SEL) in schools:
- Self-awareness: Understanding one’s own emotions, thoughts, and values.
- Self-management: Effectively managing one’s emotions, thoughts, and behaviors.
- Social awareness: Showing empathy and understanding for others.
- Relationship skills: Building and maintaining healthy relationships.
- Responsible decision-making: Making ethical, constructive choices for oneself and in support of others.
In the context of comprehensive school-based mental health, the CASEL framework provides a structured approach to nurturing students’ emotional intelligence, resilience, and interpersonal skills, which are vital for mental health well-being.
Developed by the Collaborative for Academic, Social, and Emotional Learning
https://case.org/fundamentals-of-sel/
This page offers a quick start guide to social-emotional learning (SEL). Here you will find definitions, a look at what the research says, information on how SEL supports equity, resources for speaking up for SEL, and more.
Developed by the Collaborative for Academic, Social, and Emotional Learning
https://casel.org/systemic-implementation/
Here you will find information, resources, and tools for systemic implementation of SEL at all levels – from classrooms and school communities all the way up to state and federal levels.
Developed by the Collaborative for Academic, Social, and Emotional Learning
https://signaturepractices.casel.org/
Three evidence-based practices serve as an on-ramp for integrating SEL into daily practices that foster collaborative and supportive learning and working environments.
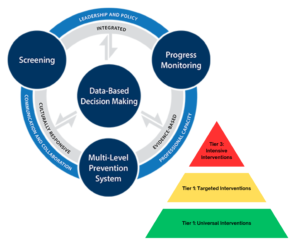
Multi-Tiered Systems of Support (MTSS)
Multi-Tiered System of Support (MTSS) is a comprehensive framework used in educational settings to provide targeted support to all students.
It integrates academic, behavioral, and social-emotional learning into a unified system and features a tiered approach:
- Tier 1 focuses on universal student support, encompassing high-quality instruction and a positive school climate.
- Tier 2 offers targeted interventions for students who require additional support beyond the universal level.
- Tier 3 provides intensive, individualized interventions for students with the most significant needs.
MTSS emphasizes data-driven decision-making, regular student progress monitoring, and evidence-based strategies and interventions at each tier to proactively identify and address student needs for academic, behavioral, and social success.
Developed by the Center on Multi-Tiered Systems of Support
https://mtss4success.org/essential-components
This resource breaks down the MTSS framework and looks at the core components, including the commonly used pyramid representing a multi-tiered prevention and response system. Here, you will find resources and guides for each of the four elements of MTSS implementation, including 1) screening, 2) multi-tiered prevention systems, 3) progress monitoring, and 4) data-based decision-making.
Developed by Panorama Education
https://www.panoramaed.com/blog/mtss-comprehensive-guide
This guide provides an overview of MTSS in schools and includes examples of how different states and school communities have adapted the framework to align with their needs.
Developed by the I-MTSS Research Network
A collection of resources that explores MTSS from an integrated approach (expanding beyond the commonly known pyramid). Here, you’ll find briefs that break down the naming, history, and concepts of tiered prevention frameworks and resources for state leaders and districts.
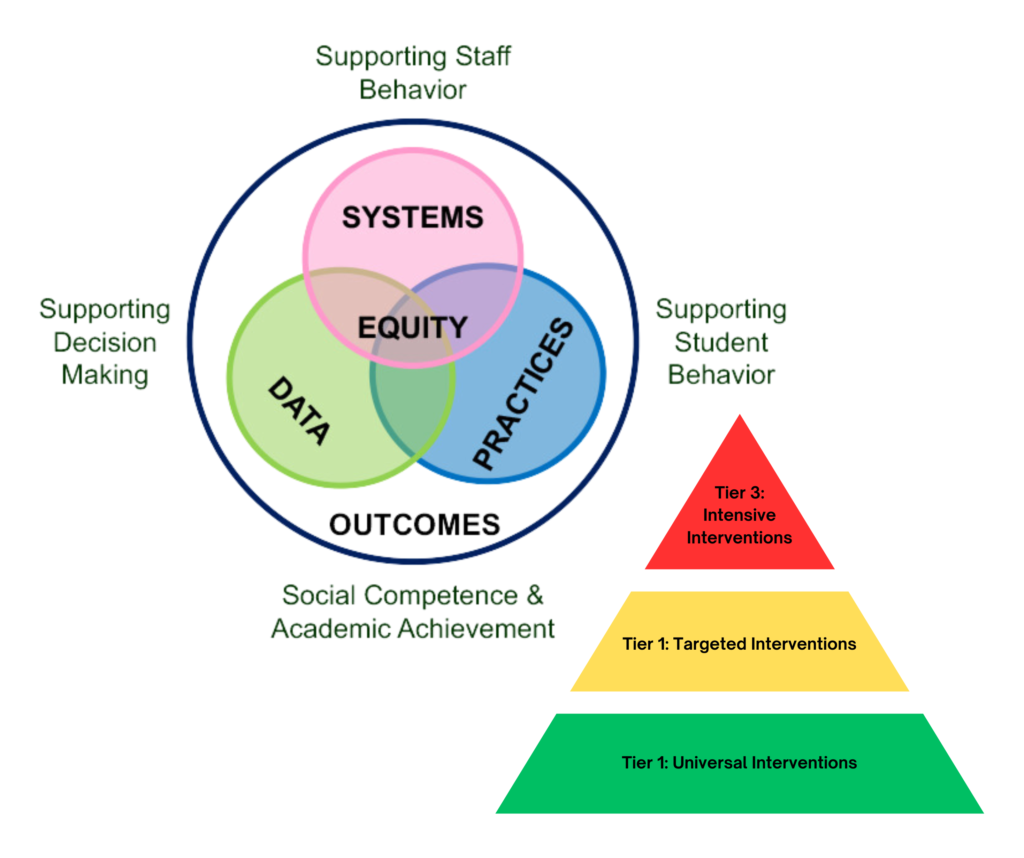
Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS)
Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS) is an evidence-based framework focused on promoting positive behavior and creating a supportive school climate. Similar to MTSS, it operates on a tiered system, with the first tier providing universal supports for all students, the second offering targeted supports for those at risk of behavioral challenges, and the third delivering intensive, individualized interventions for those with significant needs. PBIS emphasizes the proactive teaching of positive behaviors, reinforcing appropriate behavior, and data-driven decision-making.
Developed by the Center on Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports
https://www.pbis.org/pbis/getting-started
This resource helps you implement PBIS step-by-step, whether as a classroom teacher, school leader, district, or state leader.
Developed by the Center on Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports
https://www.pbis.org/resource-type/blueprints
Here, you will find blueprints for implementing and evaluating PBIS, strategies for professional development and staff training for PBIS, and more.
Developed by the Center on Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports
https://www.pbis.org/resource-type/practice-guides
A collection of practice guides on various strategies to support effective PBIS implementation.