Using GIS to Select Locations for New “Team Up. Pressure Down” for Pharmacies
Submission Date: July 2019
State/Territory Submitted on the Behalf of: Montana
States/Territories Involved: Montana
Funding Source: CDC
CDC Funding:Yes
CDC Funding (Specified):(1305) State Public Health
Domain Addressed:Epidemiology and Surveillance
Public Health Issue:Blood pressure medication nonadherence is a leading contributor to poor blood pressure control among persons treated for hypertension.
Studies have shown significant improvements in blood pressure control when healthcare teams include pharmacists. Million Hearts® “Team Up. Pressure Down.” (TUPD) is a nationwide program that uses a team-based approach and enhanced patient-pharmacist engagement to improve levels of medication adherence in the community.
The TUPD program offers resources to support pharmacists in providing counseling services to their patients with hypertension. The goal is to improve medication adherence by helping people with high blood pressure take a more active role in self-management efforts and increase interaction with their pharmacists.
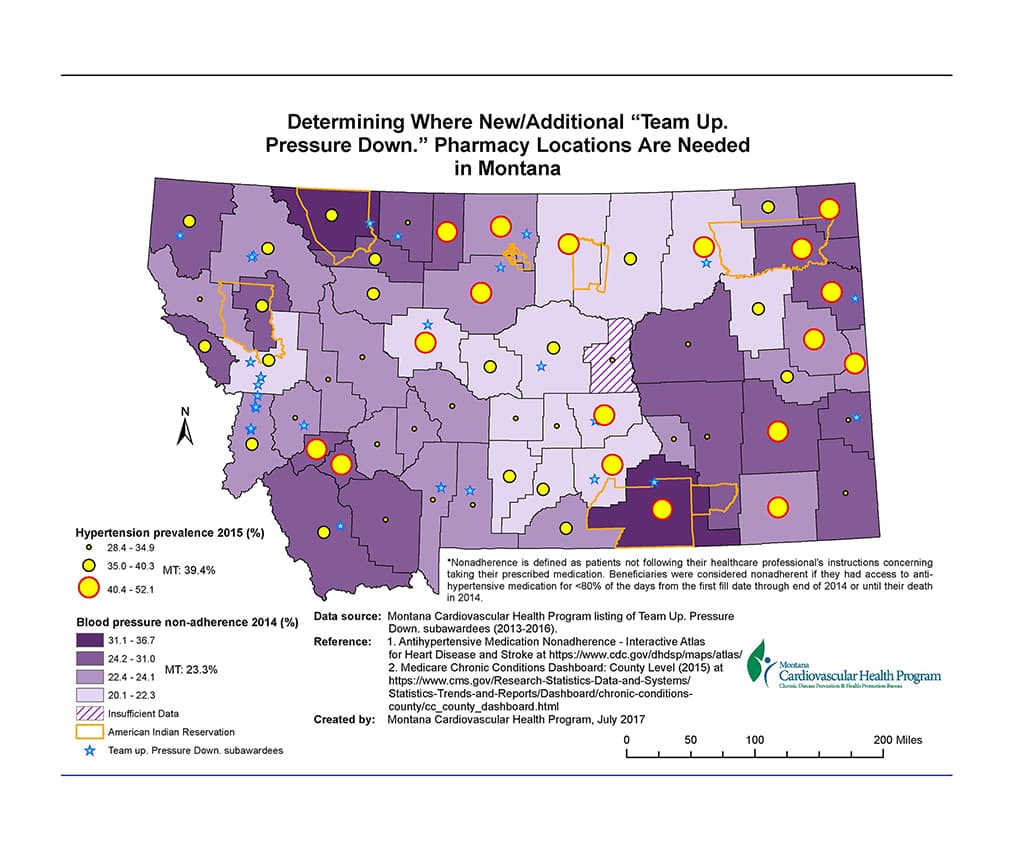
Program Action:Montana Cardiovascular Health (CVH) Program staff used the Identify-Assess-Act framework to create maps to help identify locations for new TUPD pharmacies in Montana.
- The “identify-assess-act” approach was introduced in the GIS Capacity Building Project that the Montana CVH Program staff attended in 2016.
Staff developed maps depicting the burden of hypertension prevalence, medication nonadherence rates among Medicare Part D beneficiaries age 65 years and older, and locations of existing TUPD pharmacies.
Data were obtained from the CDC’s Atlas of Heart Disease and Stroke and an inventory of pharmacies providing the TUPD intervention.
After identifying communities with heavy burdens of hypertension and poor medication adherence among Medicare beneficiaries, and no existing TUPD pharmacies, MT CVH Program staff expanded locations for new TUPD pharmacies to these communities.
Impact/Accomplishments:After pharmacists initiated consultations and distribution of Million Hearts® TUPD patient education materials, blood pressure medication adherence improved among people using community pharmacies in rural MT.
During a two-year period, the percentage of participating patients who achieved blood pressure medication adherence improved from 73% to 89%, and adherence improved in 15 of the 17 participating pharmacies. In a statewide assessment, TUPD-funded pharmacies were significantly more likely than non-TUPD-funded pharmacies to provide prescription synchronization and medication management with feedback to the patient’s physician.[i]
GIS and maps were used to identify counties with a high burden of hypertension and poor medication adherence to expand TUPD intervention to communities in need.
The Montana CVH Program is currently using GIS and maps to identify new locations for pharmacies that will focus on improving cholesterol medication adherence in addition to blood pressure control.
[i] Oser CS, Fogle CC, Bennett JA. A Project to Promote Adherence to Blood Pressure Medication Among People Who Use Community Pharmacies in Rural Montana, 2014–2016. Prev Chronic Dis 2017;14:160409. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5888/pcd14.160409
Program Areas:Epidemiology and Surveillance
State Contact Information:
MT
Carrie S. Oser
Montana Department of Public Health and Human Services
406-444-4002
coser@mt.gov
